Google Translate switches to Neural Machine Translations
Google announced yesterday that it switched the algorithm that powers its Google Translate service to Neural Machine Translations for eight language pairs, promising that more will follow over time.
Google Translate is a useful translation service that is built-in to Google Chrome but also available as a web service and as mobile apps. This first step into the future of Google Translate enables the functionality for the mobile apps and Web service. What's not yet include are web site translations but that is to follow eventually as well.
Neural Machine Translation has been enabled for the following languages: English, French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Turkish. These languages cover 35% of all Google Translate queries according to Google.
Today we’re putting Neural Machine Translation into action with a total of eight language pairs to and from English and French, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Chinese, Japanese, Korean and Turkish. These represent the native languages of around one-third of the world's population, covering more than 35% of all Google Translate queries!
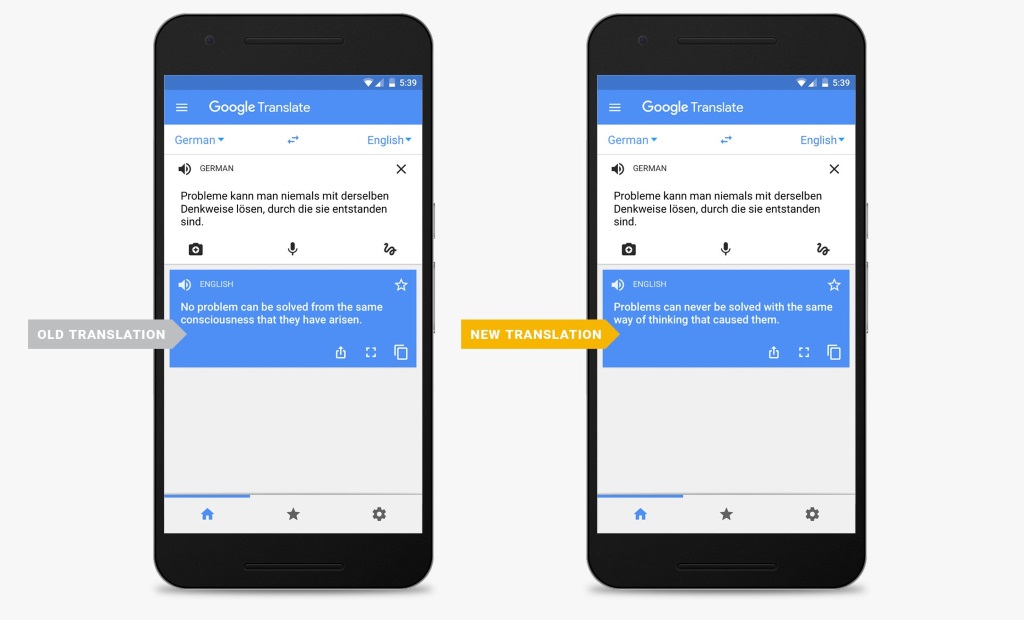
We talked about the switch to neural networks before in regards to Google Translate, and suggest you check out the initial article that provides details on how neural networks differ from traditional computer powered translations.
Only this much: One of the core differences is that neural machine translation looks at the sentence as a whole instead of just individual words or phrases. This improves the translation significantly according to Google as context is better understood which in turn produces better translated sentences.
At a high level, the Neural system translates whole sentences at a time, rather than just piece by piece. It uses this broader context to help it figure out the most relevant translation, which it then rearranges and adjusts to be more like a human speaking with proper grammar. Since it’s easier to understand each sentence, translated paragraphs and articles are a lot smoother and easier to read. And this is all possible because of end-to-end learning system built on Neural Machine Translation, which basically means that the system learns over time to create better, more natural translations.
While your mileage may vary, neural network translation improves the quality of the translated text significantly when compared to Google Translate's previously used translation algorithm.
Companies with access to Google's Cloud Translation API may use the new translation system as of today as well.
Closing Words
Google Translate was always one of the better translation services on the Internet. While far from perfect, it usually produced better or at least similar results than comparable services. The switch to Neural Machine Translations will improve translations significantly. While limited to eight languages currently only, the new system will be available for all 103 languages that Google Translate supports eventually.
Now You: What's your take on the quality of the "new" translation algorithm?
This article was first seen on ComTek's "TekBits" Technology News

- Log in to post comments