How to make Windows 10’s search lightning fast and more useful
I like the search in Windows 10 even though I had to tweak it quite a bit to make it behave the way I want it to and am running into search not working issues from time to time.
One thing that I like about it in particular is that it highlights the main results better. This is a small change that puts the focus on the first result and since search gets it right most of the time, it is easier to recognize it and select it with a tap on the enter key.
Anyway, the search is not optimized for speed by default which can be largely attributed to it trying to find web results as well as local results.
Since I don't consider web results useful at all, I have disabled the feature completely. If I want to search for something on the Web, I do so using a web browser which is open 24/7 anyway.
The next thing I did was optimize the locations that Windows indexes. The operating system indexes several by default including the complete user folder.
While that may not be as bad as it sounds, you will find many locations in the user folder that you may not want indexed or returned by search. For instance, you may have programming project directories and repositories there with thousands of files and directories, or other larger file collections that you have no interest in being returned by Windows 10's search.
There is also the AppData folder with hundreds of thousands of files, for instance web browser cache and cookies.
When it comes to the list of indexed files, it is best to only include locations that you want results to be returned from.
If you don't use Internet Explorer for instance, you may not want Internet Explorer favorites to be returned, ever. That's however one of the default locations included automatically by search indexing.
Manage search Indexing Options on Windows 10
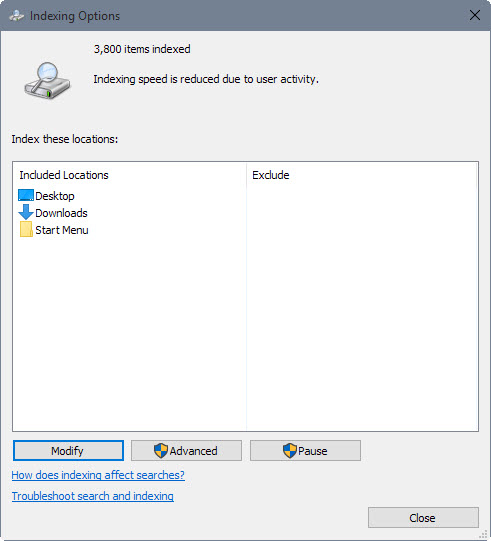
Do the following to open the Indexing Options:
- Use Windows-Pause to open the System control panel.
- Click on "All control panel items" in the location bar at the top.
- Locate and click on Indexing Options.
The window that opens displays all locations that are included by Windows 10's search indexer. The exclude listing next to each location lists subfolders of that location that are blocked from the indexer.
To get started click on modify to open the list of indexed locations and a folder browser to select new ones.
First thing you may want to do there is to click on "show all locations" as Windows hides some. A click on a location that is included jumps to it in the "change selected locations" pane which is the fastest method to uncheck them.
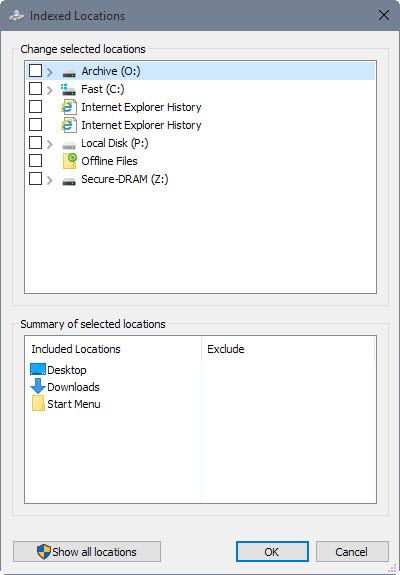
The indexer lacks a search option to find locations quickly which means that you need to click your way through the structure to include new locations.
Tips:
- Portable software is usually not included by search by default unless you have placed the programs in the user folder. Simply add the root folder of your portable software collection to the index to gain access to all programs stored in it using Windows Search.
- The exclude option is powerful and it makes sense to make use of it to block folders from being indexed. For instance, while you want to index the user folder, you may disable the indexing of folders listed in it you don't require them to be included in search.
- Some files and programs get indexed automatically. You may launch msconfig.exe or Settings at all time even if you disable all locations in the Indexing Options.
Once you have added all locations you want included, click on ok to get back to the main menu. There you need to click on the advanced button to manage advanced settings.
You find two interesting options there. First, you may move the location of the index to another drive. This can be useful if a faster drive is available that you could store the index on to speed it up further.
File Types
Second, you may want to open file types and disable those that you don't require.There is no option to disable all file types and select the ones you want only, which means lots of clicking if you want to go down that route.
I suggest you try the search first to see how fast it is. Disabling certain file types prevents them from being tracked which may reduce search pollution.
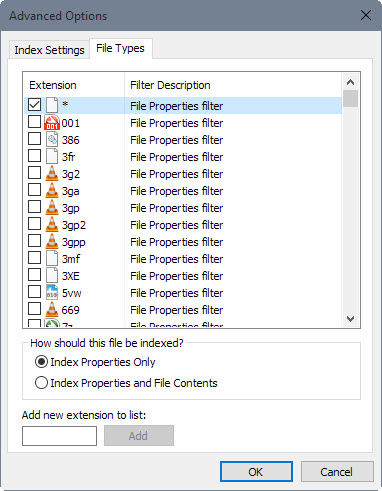
Windows Search distinguishes between indexing file properties only, or file properties and file contents. For example, Search may index Word document content automatically and return results when you search.
Properties include metadata only which may include the file name, title or author while file contents the actual (text) contents of files.
Rebuilding
Search Index needs to rebuild whenever you make modifications in Indexing Options. You can run a manual rebuild at any time from the advanced menu.
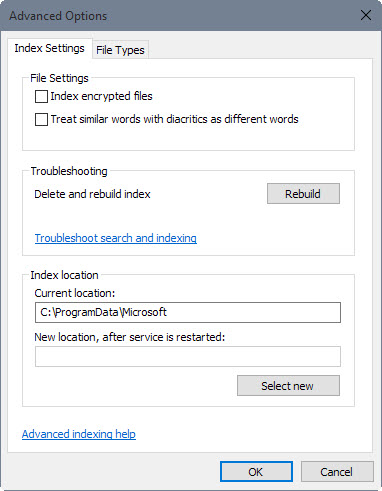
There you find options to troubleshoot search and indexing as well which launches a small program that checks common problems and attempts to fix them if found.
Closing Words
Third-party desktop search programs for Windows are a great alternative as they give you more control over the indexing and are often faster and more reliable than Windows Search.
Now You: Are you using Windows Search or a third-party search program?
This article was first seen on ComTek's "TekBits" Technology News

- Log in to post comments